This principle requires accountants to use the same reporting method procedures across all the financial statements prepared. Though it is similar to the second principle, it narrows in specifically on financial reports—ensuring any report prepared by one company can be easily compared to one another. I hope this piece has been insightful and that you’ve learned what accounting concepts and principles entail. The going concern assumption assumes that a business will continue to operate till the end of time. This principle allows us accountants to prepare our financial statements as if the company will continue its operations in the foreseeable future. Accounting concepts and principles are a set of rules and assumptions that are necessary to set a standard while recording financial transactions as well as maintaining books of accounts in the business.
Best Online Bookkeeping Services of 2024
Generally accepted accounting principles (GAAP) are uniform accounting principles for private companies and nonprofits in the U.S. These principles are largely set by the Financial Accounting Standards Board (FASB), an independent nonprofit organization whose members are chosen by the Financial Accounting Foundation. Accounting information is not absolute or concrete, and standards are developed to minimize the negative effects of inconsistent data. Without these rules, comparing financial statements among companies would be extremely difficult, even within the same industry. Many accounting practices have been simplified with the help of accounting computer-based software. These systems can be cloud based and available on demand via application or browser, or available as software installed on specific computers or local servers, often referred to as on-premise.
Get in Touch With a Financial Advisor
It is a sold text book that would require significant modification and adaptation to work for me. The text could provide a general introduction to accounting (tasks, profession, and regulation) in a more clear approach. The 35-member Financial Accounting Standards Advisory Council monitors the FASB. FASB is responsible for the Accounting Standards Codification (ASC), a centralized resource where accountants can find all current GAAP. Since much of the world uses the IFRS standard, a convergence to IFRS could benefit international corporations and investors alike. What this means is that if there is an item that is omitted from a company’s F.S., and this omission leads to a decision I was not supposed to make, if it was not omitted, it means that Item is Material.
Read 2,651 Testimonials
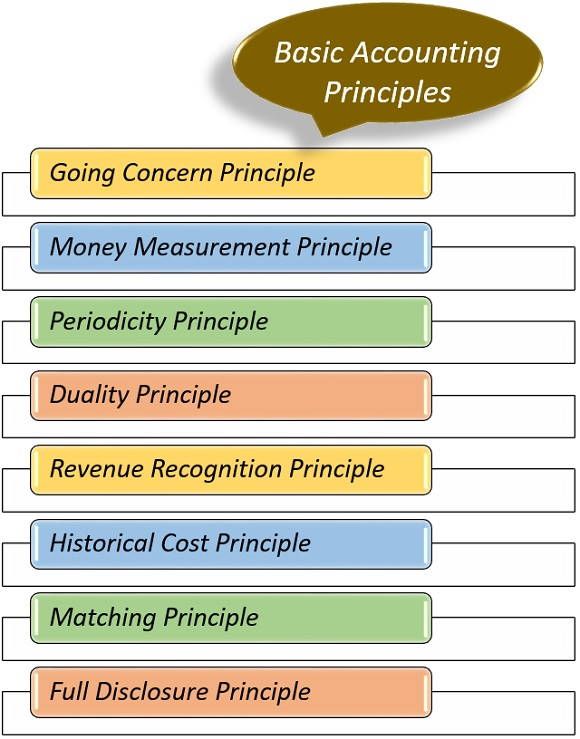
A typical illustration of this principle is a company publishing its financial statements every quarter (three months) and annually (twelve months). This principle also affects the depreciation of assets and the amortization of intangible assets. Assets are depreciated over their useful lives, reflecting their utility over time.
The 5 basic accounting concepts & principles everyone needs to know
This principle provides a more realistic valuation of assets in the normal course of business. To report a company’s net income for each month, the company will prepare adjusting entries to record each month’s share of depreciation expense, property taxes, insurance, etc. It will also prepare adjusting entries for expenses that occurred but were not paid. It also means that financial statements can be prepared for a group of separate legal corporations that are controlled by one corporation. This group of commonly owned corporations is referred to as the economic entity. The set of financial statements that reports the combined activity of the group is referred to as consolidated financial statements.
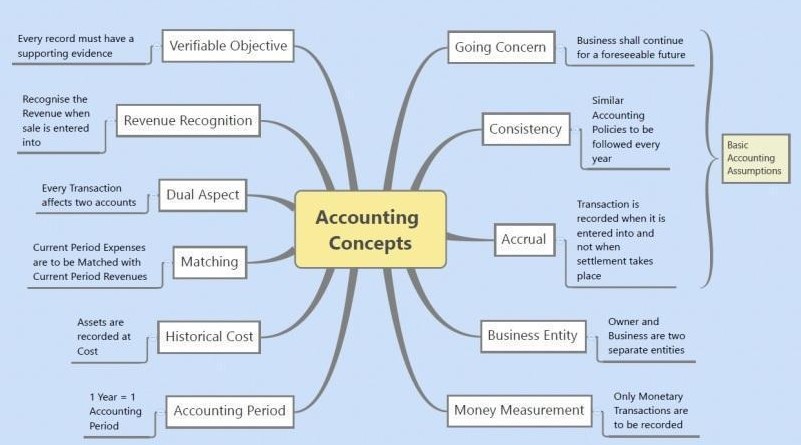
Introduction to Accounting Principles
The content is well structured, often beginning with an introduction with a case to set the stage, followed by a systematic breakdown into sections or subsections. This organization facilitates a smooth flow of information, helping readers understand the material progressively. Key concepts are appropriately highlighted, and the inclusion of relevant examples 5 principles of accounting and illustrations further enhances clarity. Despite some progress under the Norwalk Agreement, the FASB and the IASB continue to battle friction resulting from fundamental disagreements at the governance level. As of June 2024, the United States has not fully adopted IFRS principles, and domestic U.S. companies remain bound to GAAP reporting guidelines.
The ultimate goal of any set of accounting principles is to ensure that a company’s financial statements are complete, consistent, and comparable. Accounting principles are guidelines to record accurate financial data, help in financial analysis, and maintain transparency. They include Accrual, Cost, Revenue Recognition, and Objectivity principles, among others.
- This concept states that our transactions should be recorded when they occur, not when the money changes hands.
- The economic entity principle distinguishes between personal and business finances.
- Consistency allows us to compare the financial statements of different periods of the company’s existence.
- Businesses can still engage in speculation and forecasting, of course, but they cannot add this information to formal financial statements.
- In the case of rules-based methods like GAAP, complex rules can cause unnecessary complications in the preparation of financial statements.
However, the FASB and the IASB remain active collaborative partners and continue to work toward the formation of uniform international accounting standards. Also known as “pro forma” reporting, non-GAAP reporting describes financial statements, reporting standards, and disclosures that were not prepared using GAAP guidelines. They may be used by U.S. businesses and organizations not subject to GAAP requirements, or by certain international entities operating in U.S. capital markets. While it’s not necessary for you to know every in and out of GAAP unless you’re an accountant, you’re doing well to at least familiarize yourself with the basic principles. Gaining at least a conceptual understanding of the motivations behind GAAP will help you keep the financial reporting side of your business running smoothly.
These critics claim having strict rules means that companies must spend an unfair amount of their resources to comply with industry standards. Some scholars have argued that the advent of double-entry accounting practices during that time provided a springboard for the rise of commerce and capitalism. If any cost continuously changes, suppose due to a change in market prices, it will be difficult for the bookkeeper to show them in the books.
This is where these principles step in, acting as the foundation for accurate reporting. The Principle of Continuity, alternatively referred to as the Going Concern Assumption, posits that a business will sustain its operations into the foreseeable future. This assumption impacts asset valuation by allowing assets to be valued based on their continued use in the business rather than on their liquidation value, which might be lower.
Without GAAP, investors might be more reluctant to trust the information presented to them by public companies. Without that trust, fewer transactions and higher transaction costs could result, ultimately weakening the economy. GAAP also helps investors analyze companies by making it easier to perform “apples-to-apples” comparisons between one company and another, allowing for more accurate and consistent analysis. The international financial reporting standards (IFRS), set by the International Accounting Standards Board (IASB), is an alternative to GAAP that is widely used worldwide. The main objective of GAAP is to ensure that a company’s financial statements are complete, consistent, and comparable, allowing investors to analyze and extract useful information from financial statements.





